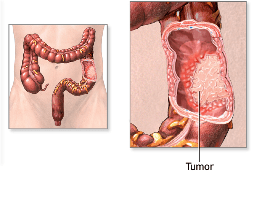
Colon cancer is a common cancer affecting the large intestine. Individuals at increased risk include those with prior history of colon cancer, a family history of colon cancer, a history of polyps, older age, diet high in protein, obesity, and smoking. In many the disease has no symptoms and is detected during a colonoscopy. In others it may present as a change in bowel habits, bleeding per rectum, unintentional weight loss, anemia, bloating, cramping, or abdominal pain.
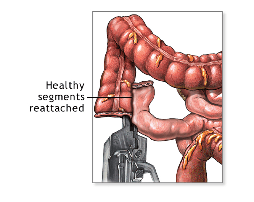
Once colon cancer is identified, the mainstay of treatment is surgical resection. The procedure is called colectomy and can be performed through an open or laparoscopic approach. Laparoscopic colectomy is associated with earlier return of bowel function, shorter hospital stay and decreased need for pain medications after surgery, as compared to open colectomy. Its safety and efficacy in treatment of colon cancer is similar to open colectomy, as investigated in numerous randomized controlled trials.
After surgery, a pathologist examines the resected cancer to determine the extent of the disease. The pathologic diagnosis along with other radiographic staging work up such as computed tomography (CT) scan will determine the stage of the cancer. Patients with advanced cancer may require additional treatment after surgery in the form of chemotherapy or radiation. Fortunately, if colon cancer is detected in an early stage, over 90% of patients will remain cancer free for at least five year or longer. For this reason, colon cancer is considered to be one of the most treatable forms of cancer.
Colon Polyps
Acolon polypis an outgrowing of the inner lining of the colon. Most polyps are non-cancerous. However, the adenomatous type of polyps can progress to form cancer. Large or flat polyps are more likely to contain cancer cells. Depending on the size and nature of the polyp, your gastroenterologist may attempt removal during colonoscopy or recommend colectomy surgery. Colectomy for colonic polyps is very similar to that of colon cancer.